HADES-M water collection from R/V Falkor FK141109 from the Mariana Trench adjacent to Guam: approximately 12 45 N and 144 50 E to 11 25 N and 144 25 E; 2014 (HADES project)
Project
| Contributors | Affiliation | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Drazen, Jeffrey C. | University of Hawai'i (UH) | Principal Investigator, Contact |
| Fryer, Patricia | University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa (HIGP) | Co-Principal Investigator |
| Jamieson, Alan | University of Aberdeen (UAberdeen-Oceanlab) | Co-Principal Investigator |
| Mayor, Dan | University of Aberdeen (UAberdeen-IBES) | Co-Principal Investigator |
| Rowden, Ashley | New Zealand National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research (NIWA) | Co-Principal Investigator |
| Ruhl, Henry | National Oceanography Centre (NOC) | Co-Principal Investigator |
| Shank, Timothy M. | Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) | Co-Principal Investigator |
| Yancey, Paul | Whitman College | Co-Principal Investigator |
| Gegg, Stephen R. | Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI BCO-DMO) | BCO-DMO Data Manager |
List of individual HADES-M samples collected on cruise FK141109 - WATER
Location:
Mariana Trench adjacent to Guam: approximately 12 45 N and 144 50 E to 11 25 N and 144 25 E
Instrument Key
CR CORE RESPIROMETER
CTD CTD
LA ABYSSAL LANDER
LH HADAL LANDER
RG ROCK GRAB
TR FISH TRAP
W WATER - SURFACE BUCKET
WT WEE TRAP
Sampling and Analytical Methodology:
Animal samples were collected using a variety of baited traps. Sediment samples were collected using megacores on a free vehicle lander. Rock samples were collected using a van veen style grab on a free vehicle lander. Water samples were collected using a conventional CTD rosette.
Investigator abbreviations are given below. These pertain to the fate of specimens and subsamples of tissues.
|
INITIAL |
NAME |
INSTITUTION |
|
AJ |
ALAN JAMIESON |
UNIVERSITY OF ABERDEEN |
|
CY |
CRAIG YOUNG |
OREGON STATE |
|
DM |
DAN MAYOR |
UNIVERSITY OF ABERDEEN |
|
JD |
JEFF DRAZEN |
UNIVERSITY OF HAWAII |
|
MG |
MACKENZIE GERRINGER |
UNIVERSITY OF HAWAII |
|
PY |
PAUL YANCEY |
WHITMAN COLLEGE |
|
SP |
STUART PIERTNEY |
UNIVERSITY OF ABERDEEN |
|
TL |
THOMAS LINLEY |
UNIVERSITY OF ABERDEEN |
|
TS |
TIM SHANK |
WHOI |
|
AD |
AMANDA DEMOPOULOS |
USGS |
|
EG |
ELEANNA GRAMMOPOULOS |
UNIVERSITY OF ABERDEEN |
Instrument Key
CR CORE RESPIROMETER
CTD CTD
LA ABYSSAL LANDER
LH HADAL LANDER
RG ROCK GRAB
TR FISH TRAP
W WATER - SURFACE BUCKET
WT WEE TRAP
WT WEE TRAP
CORING RESPIROMETER – A free vehicle lander equipped with 4 megacore tubes that are pushed into the sediments by a drive motor after the vehicle lands on the seafloor. Each tube is equipped with an oxygen optode and water mixing pump to measure sediment community oxygen consumption in each core. Each core is trapped by a standard megacore core catching device and returned to the surface with the lander. The instrument also includes an oxygen sensor for the ambient bottom water.
CTD – Conventional CTD rosette was used to take water samples to 5000m depth at several stations.
ABYSSAL LANDER – A free vehicle lander equipped with a still image camera and baited to attract scavengers. Images were taken once every minute. It is rated to 6000m.
HADAL LANDER – A free vehicle lander equipped with a digital video camera and baited to attract scavengers. One minute of video was recorded every 2.5 or every 5 minutes. It is rated to 11000m.
FISH TRAP – A large mesh trap with two smaller PVC tube shaped amphipod traps inside that were baited to capture megafauna. It was deployed as a free vehicle lander.
WEE TRAP – Another baited trap but smaller in size than the fish trap.
Data Processing:
Direct counts and measurements of mass and length. Mass was determined aboard ship using a motion compensated scale.
BCO-DMO Processing Notes
- Generated from original file: "HADES.M deployments and samples for BCO-DMO.xlsx" contributed by Jeff Drazen
- Parameter names edited to conform to BCO-DMO naming convention found at Choosing Parameter Name
- "nd" (no data) inserted into blank cells and cells with "-"
- Dates reformatted to YYYYMMDD
| File |
|---|
HADESM_Samples_Water.csv (Comma Separated Values (.csv), 384 bytes) MD5:e146beb184a863c1e170fae1a9bce431 Primary data file for dataset ID 636788 |
| Parameter | Description | Units |
| STATION | Station Number | dimensionless |
| DEPLOYMENT | Instrument/Lander Id CR CORE RESPIROMETER | text |
| DATE | Date | YYYYMMDD |
| LATITUDE | Latitude (South is negative) | decimal degrees |
| LONGITUDE | Longitude (West is negative) | decimal degrees |
| MULTIBEAM_DEPTH | Multibeam Depth | meters |
| SAMPLE_NUMBER | SAMPLE NUMBER | dimensionless |
| PROCESSED_BY | PROCESSED BY | text |
| Dataset-specific Instrument Name | Van Veen Grab |
| Generic Instrument Name | Bottom Sediment Grab Samplers |
| Dataset-specific Description | Sampling and Analytical Methodology:
Animal samples were collected using a variety of baited traps. Sediment samples were collected using megacores on a free vehicle lander. Rock samples were collected using a van veen style grab on a free vehicle lander. Water samples were collected using a conventional CTD rosette. |
| Generic Instrument Description | These samplers are designed to collect an accurate representative sample of the sediment bottom. The bite of the sampler should be deep enough so all depths are sampled equally. The closing mechanism is required to completely close and hold the sample as well as prevent wash-out during retrieval. Likewise, during descent the sampler should be designed to minimize disturbance of the topmost sediment by the pressure wave as it is lowered to the bottom. |
| Dataset-specific Instrument Name | Water Bucket |
| Generic Instrument Name | bucket |
| Dataset-specific Description | Sampling and Analytical Methodology:
Animal samples were collected using a variety of baited traps. Sediment samples were collected using megacores on a free vehicle lander. Rock samples were collected using a van veen style grab on a free vehicle lander. Water samples were collected using a conventional CTD rosette. |
| Generic Instrument Description | A bucket used to collect surface sea water samples. |
| Dataset-specific Instrument Name | CTD Sea-Bird SBE 911plus |
| Generic Instrument Name | CTD Sea-Bird SBE 911plus |
| Dataset-specific Description | Sampling and Analytical Methodology:
Animal samples were collected using a variety of baited traps. Sediment samples were collected using megacores on a free vehicle lander. Rock samples were collected using a van veen style grab on a free vehicle lander. Water samples were collected using a conventional CTD rosette. |
| Generic Instrument Description | The Sea-Bird SBE 911 plus is a type of CTD instrument package for continuous measurement of conductivity, temperature and pressure. The SBE 911 plus includes the SBE 9plus Underwater Unit and the SBE 11plus Deck Unit (for real-time readout using conductive wire) for deployment from a vessel. The combination of the SBE 9 plus and SBE 11 plus is called a SBE 911 plus. The SBE 9 plus uses Sea-Bird's standard modular temperature and conductivity sensors (SBE 3 plus and SBE 4). The SBE 9 plus CTD can be configured with up to eight auxiliary sensors to measure other parameters including dissolved oxygen, pH, turbidity, fluorescence, light (PAR), light transmission, etc.). more information from Sea-Bird Electronics |
| Dataset-specific Instrument Name | Baited Traps |
| Generic Instrument Name | Flounder Trap |
| Dataset-specific Description | Sampling and Analytical Methodology:
Animal samples were collected using a variety of baited traps. Sediment samples were collected using megacores on a free vehicle lander. Rock samples were collected using a van veen style grab on a free vehicle lander. Water samples were collected using a conventional CTD rosette. |
| Generic Instrument Description | Based on an historical design used previously in the Gulf of Maine to target Winter Flounder, this experimental trap is a converted lobster trap fitted with a standard crab hoop acting as one long entrance. The crab hoop measures 8 inches across and 2 1/2 inches in height and it was hoped that this hoop would allow flatfish, crabs and some finfish to enter while excluding most lobsters. These traps were built by Kelo Pinkham and Jim Lowe, from Boothbay, Maine. Collapsible square fish traps are also available commercially for eel, crawfish and flounder. |
| Dataset-specific Instrument Name | HADAL-Lander |
| Generic Instrument Name | HADAL-Lander |
| Dataset-specific Description | Sampling and Analytical Methodology:
Animal samples were collected using a variety of baited traps. Sediment samples were collected using megacores on a free vehicle lander. Rock samples were collected using a van veen style grab on a free vehicle lander. Water samples were collected using a conventional CTD rosette. |
| Generic Instrument Description | The HADAL-Lander is a free-falling baited lander composed of two major components; the scientific payload and delivery system.
HADAL-Lander A
HADAL-Lander-B |
| Dataset-specific Instrument Name | Mega Cores |
| Generic Instrument Name | Multi Corer |
| Dataset-specific Description | Sampling and Analytical Methodology:
Animal samples were collected using a variety of baited traps. Sediment samples were collected using megacores on a free vehicle lander. Rock samples were collected using a van veen style grab on a free vehicle lander. Water samples were collected using a conventional CTD rosette. |
| Generic Instrument Description | The Multi Corer is a benthic coring device used to collect multiple, simultaneous, undisturbed sediment/water samples from the seafloor. Multiple coring tubes with varying sampling capacity depending on tube dimensions are mounted in a frame designed to sample the deep ocean seafloor. For more information, see Barnett et al. (1984) in Oceanologica Acta, 7, pp. 399-408. |
| Dataset-specific Instrument Name | Niskin |
| Generic Instrument Name | Niskin bottle |
| Dataset-specific Description | Sampling and Analytical Methodology:
Animal samples were collected using a variety of baited traps. Sediment samples were collected using megacores on a free vehicle lander. Rock samples were collected using a van veen style grab on a free vehicle lander. Water samples were collected using a conventional CTD rosette. |
| Generic Instrument Description | A Niskin bottle (a next generation water sampler based on the Nansen bottle) is a cylindrical, non-metallic water collection device with stoppers at both ends. The bottles can be attached individually on a hydrowire or deployed in 12, 24, or 36 bottle Rosette systems mounted on a frame and combined with a CTD. Niskin bottles are used to collect discrete water samples for a range of measurements including pigments, nutrients, plankton, etc. |
FK141109
| Website | |
| Platform | R/V Falkor |
| Report | |
| Start Date | 2014-11-09 |
| End Date | 2014-12-09 |
| Description | The very deepest reaches of the sea are one of the planet’s last true frontiers. That’s mostly because a lack of support for needed technological advancements and vehicles has severely limited access to depths beyond 7,000 meters. But the situation is finally beginning to change, and SOI is helping push the process forward. In November, the institute collaborated with a group of biologists and geologists working aboard R/V Falkor to conduct a new study of one of the deepest places in the world.
The team deployed SOI's new full-ocean-depth landers—frames equipped with cameras, sensors and sample collection devices that return to the surface automatically after a set time on the seafloor—as well as three other landers, in the Mariana Trench's Sirena Deep, near Guam. The work, at depths down to almost 11,000 meters, will help answer enduring questions about the biology of such alien zones, including who lives there and how they survive the massive pressure. The research should also improve understanding of the processes that control earthquake and tsunami formation, among others geological goals.
Original cruise data are available from the NSF R2R data catalog (Cruise DOI: 10.7284/900733) |
Controls on Hadal Megafaunal Community Structure: a Systematic Examination of Pressure, Food Supply, and Topography (HADES)
Extracted from the NSF award abstract:
Severe technical challenges associated with the extremes of hydrostatic pressure have prevented major advances in hadal ecological studies, and relegated hadal systems to among the most poorly investigated habitats on Earth. Through this project, Hadal Ecosystems Studies (HADES) program, PIs will determine the composition and distribution of hadal species, the role of hadal pressures (piezolyte concentrations, enzyme function under pressure), food supply (distribution of POC with the abundance and biomass of trench organisms, and metabolic rates/energetic demand), and depth/topography (genetic divergence and spatial connectivity of populations) have on impacting deep-ocean community structure. This project will examine these factors using the world's first full-ocean depth hybrid remotely operated vehicle (HROV) in conjunction with the only full-ocean depth imaging lander (Hadal-Lander). This project will provide the first seafloor data and samples in one of the world's best, yet little known trenches- the Kermadec Trench (SW Pacific Ocean). Megafaunal community structure and the relationship between POC and benthic bacterial biomass will be examined as a function of depth and location by systematic high-definition imaging and sediment/faunal sampling transects from abyssal to full trench depths both along and perpendicular to the trench axis. Population genetic approaches will provide levels of genetic divergence and evolutionarily independent lineages to assess the role of depth and topography in trenches and their adjacent abyssal plain in promoting the formation of species. Physiological constraints will be investigated by examining in-situ respiration of selected fauna and tissue concentrations of such protein stabilizers as trimethylamine oxide (TMAO), and the structural adaptations of macromolecules.
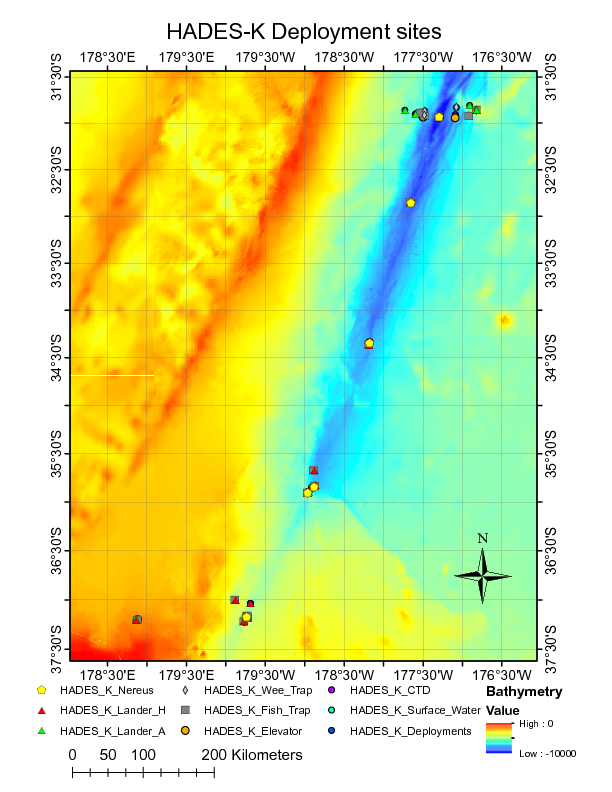
Image of NEREUS Deployment Sites. [click on the image to view a larger version]
| Funding Source | Award |
|---|---|
| NSF Division of Ocean Sciences (NSF OCE) | |
| NSF Division of Ocean Sciences (NSF OCE) | |
| NSF Division of Ocean Sciences (NSF OCE) | |
| Schmidt Ocean Institute (SOI) |
[ table of contents | back to top ]