Seawater chemistry during pCO2 flume experiments at Richard B Gump Research Station in Moorea, French Polynesia from May to June of 2014
Project
Programs
| Contributors | Affiliation | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Edmunds, Peter J. | California State University Northridge (CSUN) | Principal Investigator |
| Carpenter, Robert | California State University Northridge (CSUN) | Co-Principal Investigator |
| Srednick, Griffin | California State University Northridge (CSUN) | Technician |
| Vaughan, Megan | California State University Northridge (CSUN) | Technician |
| York, Amber D. | Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI BCO-DMO) | BCO-DMO Data Manager |
Abstract
These data were utilized in Evensen & Edmunds, 2016.
Other datasets utilized in Evensen and Edmunds, 2016:
* Coral growth - https://www.bco-dmo.org/dataset/683932
* Field data - coral colony interactions - https://www.bco-dmo.org/dataset/684528
These data are from an experiment performed in Moorea in May-June 2014. Aggregates of 12 colonies were placed in one of six tanks (1 aggregate per tank) at either ambient (~400 µatm) or high (~1100 µatm) pCO2 (3 tanks per treatment) for 28 days. Buoyant weights of the corals were recorded before and after incubation. See dataset "pCO2 flume May to Jun 2014 coral growth" https://www.bco-dmo.org/dataset/683932 for coral growth data during this experiment). The difference between the initial and final buoyant weight was converted to dry skeletal weight using the aragonite density of 2.93 g cm-3, in accordance with the mineral form of CaCO3 deposited by Pocillopora and Acropora. Rates of net calcification (Gn) were normalized to the tissue area, which was estimated using wax dipping (Stimson and Kinzie 1991).
In order to allow full comparability with other ocean acidification data sets, the R package seacarb (Lavigne and Gattuso, 2013) was used to compute a complete and consistent set of carbonate system variables, as described by Nisumaa et al. (2010). pH was measured daily with the Orion 3-star pH sensor (with DG115-SC probe, Mettler Toldeo). Total alkalinity of seawater was measured from 50 mL samples taken every two days by open-cell potentiometric titrations using an automated titrator (T50 Mettler-Toledo). Aragonite and pCO2 parameters were calculated from measurements of total alkalinity, salinity, and pH (Gattuso et al. 2015).
Physical conditions in the flumes were analyzed with a two-way ANOVA, with pCO2 as a fixed
effect and flume a random factor nested in each treatment. Calcification, horizontal growth, and
vertical growth collectively were analyzed in multivariate framework using mixed effects
PERMANOVA, with pCO2 as a fixed, between plot effect, flume as a random factor nested in
each treatment, and arrangement as a fixed, split-plot effect in each flume.
BCO-DMO Data Manager Processing Notes:
* added a conventional header with dataset name, PI name, version date
* modified parameter names to conform with BCO-DMO naming conventions
* blank values replaced with no data value 'nd'
* All values were rounded to three decimal places if more than that.
* latitude and longitude added for experiment location
| File |
|---|
seawater_chem.csv (Comma Separated Values (.csv), 7.43 KB) MD5:3eb3f33d40faecae3408116ebeceb9d5 Primary data file for dataset ID 684541 |
| Parameter | Description | Units |
| site | Location of flume; MCR is shorthand for Moorea Coral Reef Long-Term Ecological Research site | unitless |
| lat | Latitude of sampling location | decimal degrees |
| lon | Longitude of sampling location; west is negative | decimal degrees |
| date | Date of sample in format yyyy-mm-dd | unitless |
| flume | Flume number (2 & 4 = ambient pCO2 treatment; 1 & 3 = high pCO2 treatment) | unitless |
| treatment | pCO2 treatment in each flume (Ambient=~400 uatm; High=~1000 uatm) | unitless |
| sal | Salinity in flume | parts per thousand (ppt) |
| temp | Temperature in flume | degrees Celsius |
| pH | pH in flume | pH(total scale) |
| pCO2 | CO2 partial pressure at in situ temperature and atmospheric pressure for a given flume | micro atmospheres (uatm) |
| TA | Total alkalinity for a given flume | micromoles per kilogram of seawater (umol kgSW-1) |
| omega_aragonite | Aragonite saturation state for a given flume | dimensionless |
| Dataset-specific Instrument Name | Orion 3-stars |
| Generic Instrument Name | pH Sensor |
| Dataset-specific Description | Orion 3-stars, Thermo Scientific, USA, mounted with a combination pH probe DG115-SC, Mettler Tolde. |
| Generic Instrument Description | An instrument that measures the hydrogen ion activity in solutions.
The overall concentration of hydrogen ions is inversely related to its pH. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14 and indicates whether acidic (more H+) or basic (less H+). |
| Dataset-specific Instrument Name | T50 |
| Generic Instrument Name | Titrator |
| Dataset-specific Description | T50, Mettler-Toledo, Switzerland |
| Generic Instrument Description | Titrators are instruments that incrementally add quantified aliquots of a reagent to a sample until the end-point of a chemical reaction is reached. |
MCR_Edmunds
| Website | |
| Platform | Richard B Gump Research Station - Moorea LTER |
| Start Date | 2010-01-01 |
| End Date | 2016-12-31 |
| Description | Ongoing studies on corals |
Moorea Coral Reef Long-Term Ecological Research site (MCR LTER)
From http://www.lternet.edu/sites/mcr/ and http://mcr.lternet.edu/:
The Moorea Coral Reef LTER site encompasses the coral reef complex that surrounds the island of Moorea, French Polynesia (17°30'S, 149°50'W). Moorea is a small, triangular volcanic island 20 km west of Tahiti in the Society Islands of French Polynesia. An offshore barrier reef forms a system of shallow (mean depth ~ 5-7 m), narrow (~0.8-1.5 km wide) lagoons around the 60 km perimeter of Moorea. All major coral reef types (e.g., fringing reef, lagoon patch reefs, back reef, barrier reef and fore reef) are present and accessible by small boat.
The MCR LTER was established in 2004 by the US National Science Foundation (NSF) and is a partnership between the University of California Santa Barbara and California State University, Northridge. MCR researchers include marine scientists from the UC Santa Barbara, CSU Northridge, UC Davis, UC Santa Cruz, UC San Diego, CSU San Marcos, Duke University and the University of Hawaii. Field operations are conducted from the UC Berkeley Richard B. Gump South Pacific Research Station on the island of Moorea, French Polynesia.
MCR LTER Data: The Moorea Coral Reef (MCR) LTER data are managed by and available directly from the MCR project data site URL shown above. The datasets listed below were collected at or near the MCR LTER sampling locations, and funded by NSF OCE as ancillary projects related to the MCR LTER core research themes.
This project is supported by continuing grants with slight name variations:
- LTER: Long-Term Dynamics of a Coral Reef Ecosystem
- LTER: MCR II - Long-Term Dynamics of a Coral Reef Ecosystem
- LTER: MCR IIB: Long-Term Dynamics of a Coral Reef Ecosystem
- LTER: MCR III: Long-Term Dynamics of a Coral Reef Ecosystem
- LTER: MCR IV: Long-Term Dynamics of a Coral Reef Ecosystem
Collaborative Research: Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs: Scale Dependence and Adaptive Capacity (OA coral adaptation)
Extracted from the NSF award abstract:
This project focuses on the most serious threat to marine ecosystems, Ocean Acidification (OA), and addresses the problem in the most diverse and beautiful ecosystem on the planet, coral reefs. The research utilizes Moorea, French Polynesia as a model system, and builds from the NSF investment in the Moorea Coral Reef Long Term Ecological Research Site (LTER) to exploit physical and biological monitoring of coral reefs as a context for a program of studies focused on the ways in which OA will affect corals, calcified algae, and coral reef ecosystems. The project builds on a four-year NSF award with research in five new directions: (1) experiments of year-long duration, (2) studies of coral reefs to 20-m depth, (3) experiments in which carbon dioxide will be administered to plots of coral reef underwater, (4) measurements of the capacity of coral reef organisms to change through evolutionary and induced responses to improve their resistance to OA, and (5) application of emerging theories to couple studies of individual organisms to studies of whole coral reefs. Broader impacts will accrue through a better understanding of the ways in which OA will affect coral reefs that are the poster child for demonstrating climate change effects in the marine environment, and which provide income, food, and coastal protection to millions of people living in coastal areas, including in the United States.
This project focuses on the effects of Ocean Acidification on tropical coral reefs and builds on a program of research results from an existing 4-year award, and closely interfaces with the technical, hardware, and information infrastructure provided through the Moorea Coral Reef (MCR) LTER. The MCR-LTER, provides an unparalleled opportunity to partner with a study of OA effects on a coral reef with a location that arguably is better instrumented and studied in more ecological detail than any other coral reef in the world. Therefore, the results can be both contextualized by a high degree of ecological and physical relevance, and readily integrated into emerging theory seeking to predict the structure and function of coral reefs in warmer and more acidic future oceans. The existing award has involved a program of study in Moorea that has focused mostly on short-term organismic and ecological responses of corals and calcified algae, experiments conducted in mesocosms and flumes, and measurements of reef-scale calcification. This new award involves three new technical advances: for the first time, experiments will be conducted of year-long duration in replicate outdoor flumes; CO2 treatments will be administered to fully intact reef ecosystems in situ using replicated underwater flumes; and replicated common garden cultivation techniques will be used to explore within-species genetic variation in the response to OA conditions. Together, these tools will be used to support research on corals and calcified algae in three thematic areas: (1) tests for long-term (1 year) effects of OA on growth, performance, and fitness, (2) tests for depth-dependent effects of OA on reef communities at 20-m depth where light regimes are attenuated compared to shallow water, and (3) tests for beneficial responses to OA through intrinsic, within-species genetic variability and phenotypic plasticity. Some of the key experiments in these thematic areas will be designed to exploit integral projection models (IPMs) to couple organism with community responses, and to support the use of the metabolic theory of ecology (MTE) to address scale-dependence of OA effects on coral reef organisms and the function of the communities they build.
The following publications and data resulted from this project:
Comeau S, Carpenter RC, Lantz CA, Edmunds PJ. (2016) Parameterization of the response of calcification to temperature and pCO2 in the coral Acropora pulchra and the alga Lithophyllum kotschyanum. Coral Reefs 2016. DOI 10.1007/s00338-016-1425-0.
calcification rates (2014)
calcification rates (2010)
Comeau, S., Carpenter, R.C., Edmunds, P.J. (2016) Effects of pCO2 on photosynthesis and respiration of tropical scleractinian corals and calcified algae. ICES Journal of Marine Science doi:10.1093/icesjms/fsv267.
respiration and photosynthesis I
respiration and photosynthesis II
Evensen, N.R. & Edmunds P. J. (2016) Interactive effects of ocean acidification and neighboring corals on the growth of Pocillopora verrucosa. Marine Biology, 163:148. doi: 10.1007/s00227-016-2921-z
coral growth
seawater chemistry
coral colony interactions
Long Term Ecological Research network (LTER)
adapted from http://www.lternet.edu/
The National Science Foundation established the LTER program in 1980 to support research on long-term ecological phenomena in the United States. The Long Term Ecological Research (LTER) Network is a collaborative effort involving more than 1800 scientists and students investigating ecological processes over long temporal and broad spatial scales. The LTER Network promotes synthesis and comparative research across sites and ecosystems and among other related national and international research programs. The LTER research sites represent diverse ecosystems with emphasis on different research themes, and cross-site communication, network publications, and research-planning activities are coordinated through the LTER Network Office.
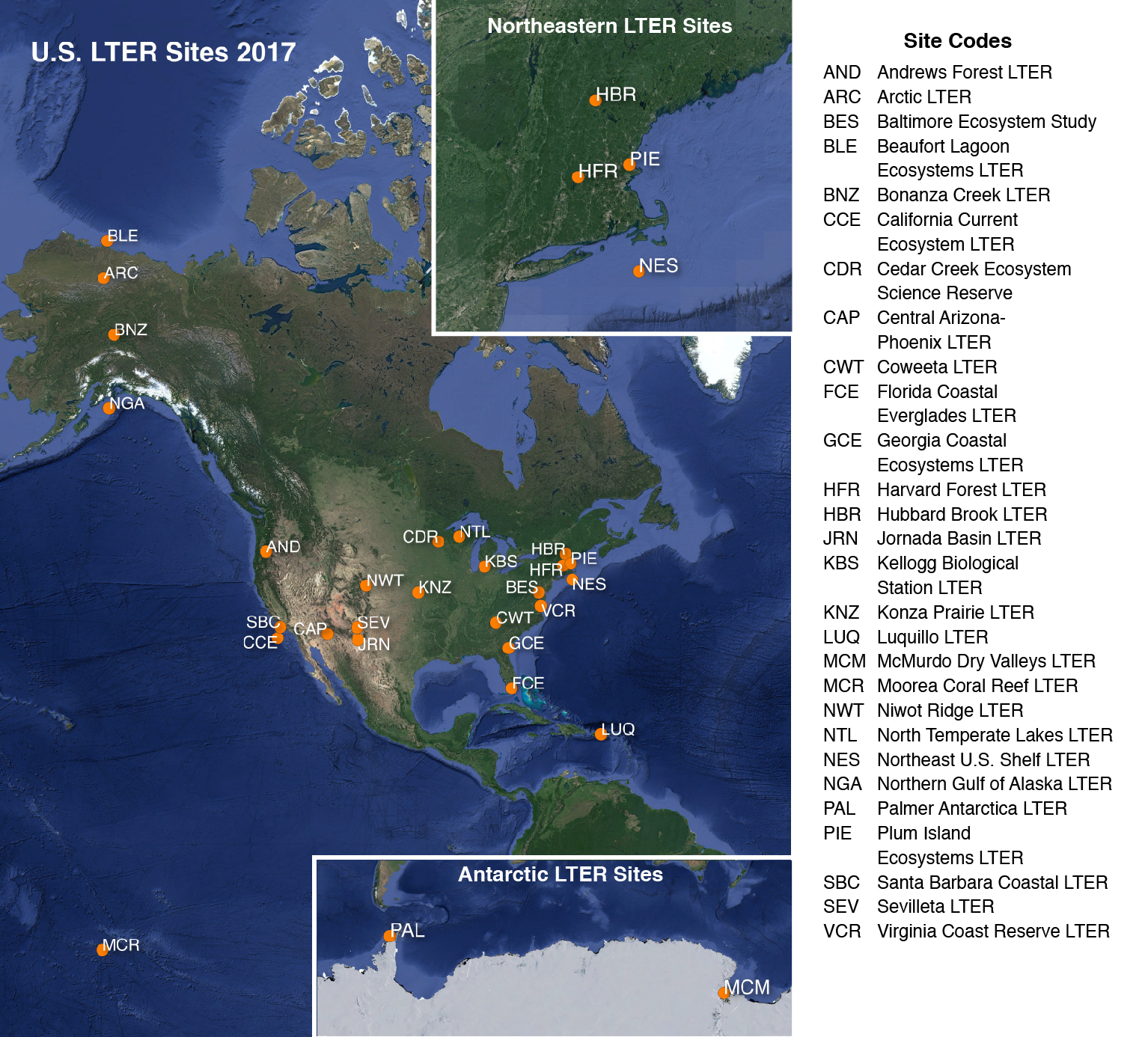
2017 LTER research site map obtained from https://lternet.edu/site/lter-network/
Science, Engineering and Education for Sustainability NSF-Wide Investment (SEES): Ocean Acidification (formerly CRI-OA) (SEES-OA)
NSF Climate Research Investment (CRI) activities that were initiated in 2010 are now included under Science, Engineering and Education for Sustainability NSF-Wide Investment (SEES). SEES is a portfolio of activities that highlights NSF's unique role in helping society address the challenge(s) of achieving sustainability. Detailed information about the SEES program is available from NSF (https://www.nsf.gov/funding/pgm_summ.jsp?pims_id=504707).
In recognition of the need for basic research concerning the nature, extent and impact of ocean acidification on oceanic environments in the past, present and future, the goal of the SEES: OA program is to understand (a) the chemistry and physical chemistry of ocean acidification; (b) how ocean acidification interacts with processes at the organismal level; and (c) how the earth system history informs our understanding of the effects of ocean acidification on the present day and future ocean.
Solicitations issued under this program:
NSF 10-530, FY 2010-FY2011
NSF 12-500, FY 2012
NSF 12-600, FY 2013
NSF 13-586, FY 2014
NSF 13-586 was the final solicitation that will be released for this program.
PI Meetings:
1st U.S. Ocean Acidification PI Meeting(March 22-24, 2011, Woods Hole, MA)
2nd U.S. Ocean Acidification PI Meeting(Sept. 18-20, 2013, Washington, DC)
3rd U.S. Ocean Acidification PI Meeting (June 9-11, 2015, Woods Hole, MA – Tentative)
NSF media releases for the Ocean Acidification Program:
Press Release 10-186 NSF Awards Grants to Study Effects of Ocean Acidification
Discovery Blue Mussels "Hang On" Along Rocky Shores: For How Long?
Press Release 13-102 World Oceans Month Brings Mixed News for Oysters
| Funding Source | Award |
|---|---|
| NSF Division of Ocean Sciences (NSF OCE) | |
| NSF Division of Ocean Sciences (NSF OCE) |
[ table of contents | back to top ]